 Product Center
Product Center


Microwave active module

Microwave passive components

Power Amplifier

Rf matrix & Intermodulation test system

EMC testing system

High Intensity Radiation Field (HIRF) system

Integrated anti-drone system
Product Center
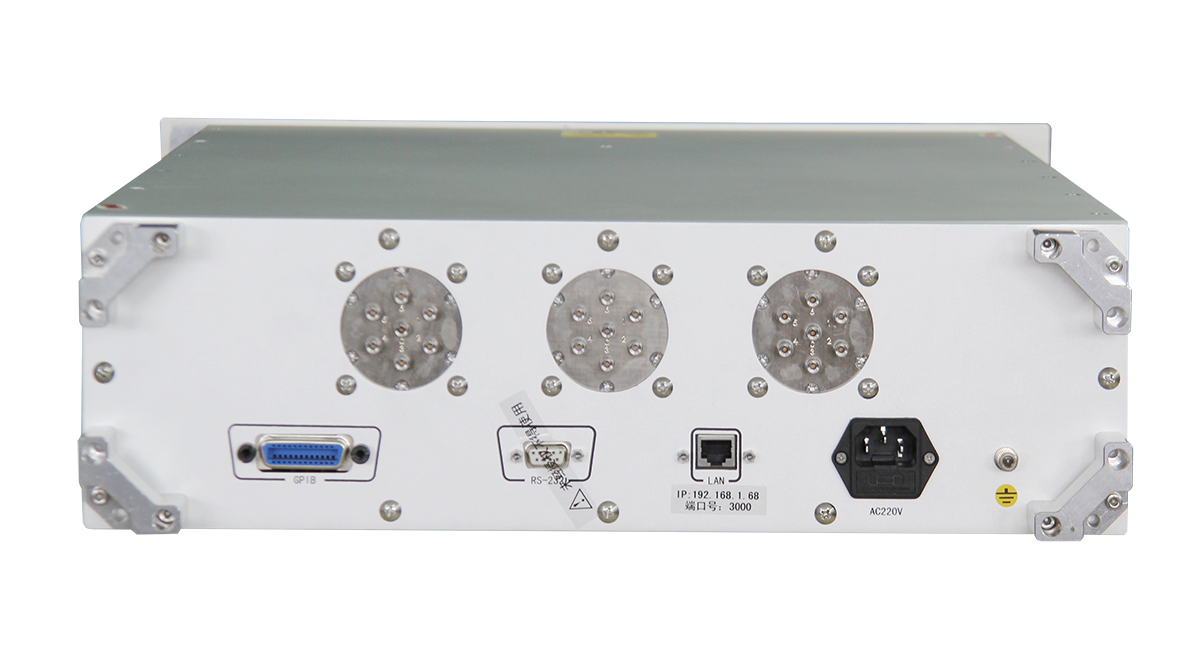
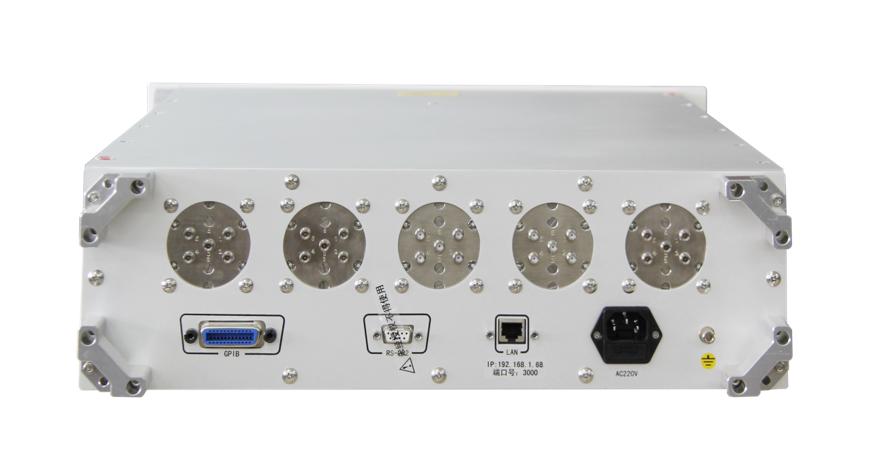










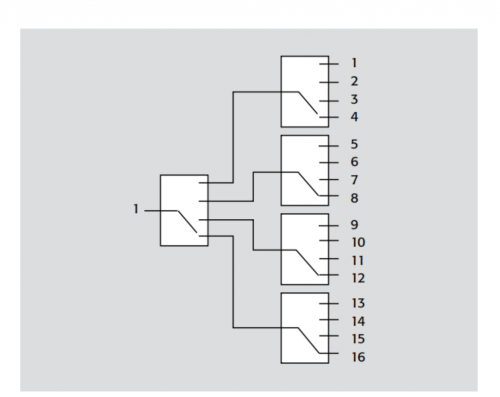

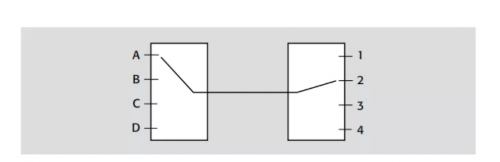
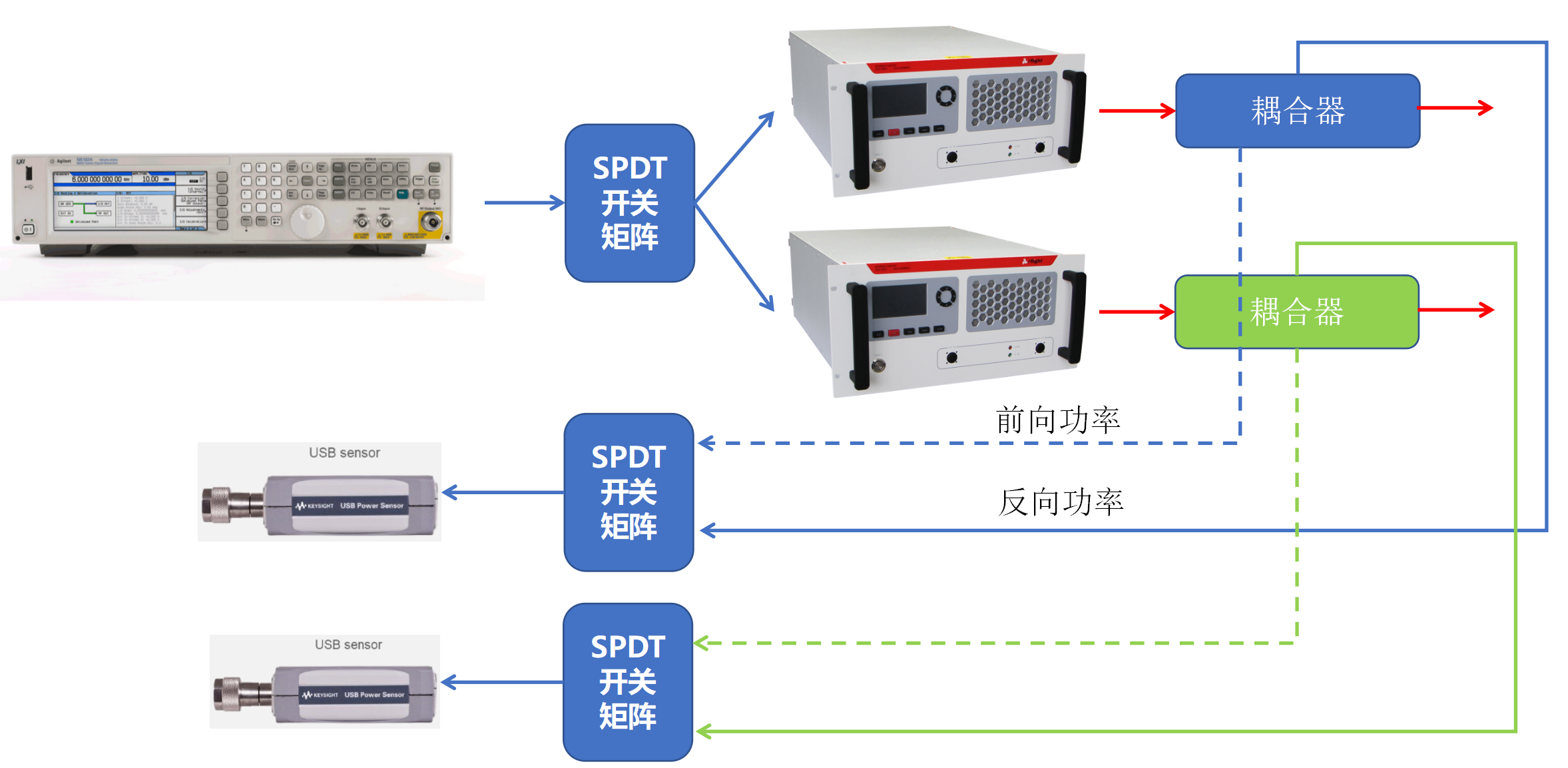
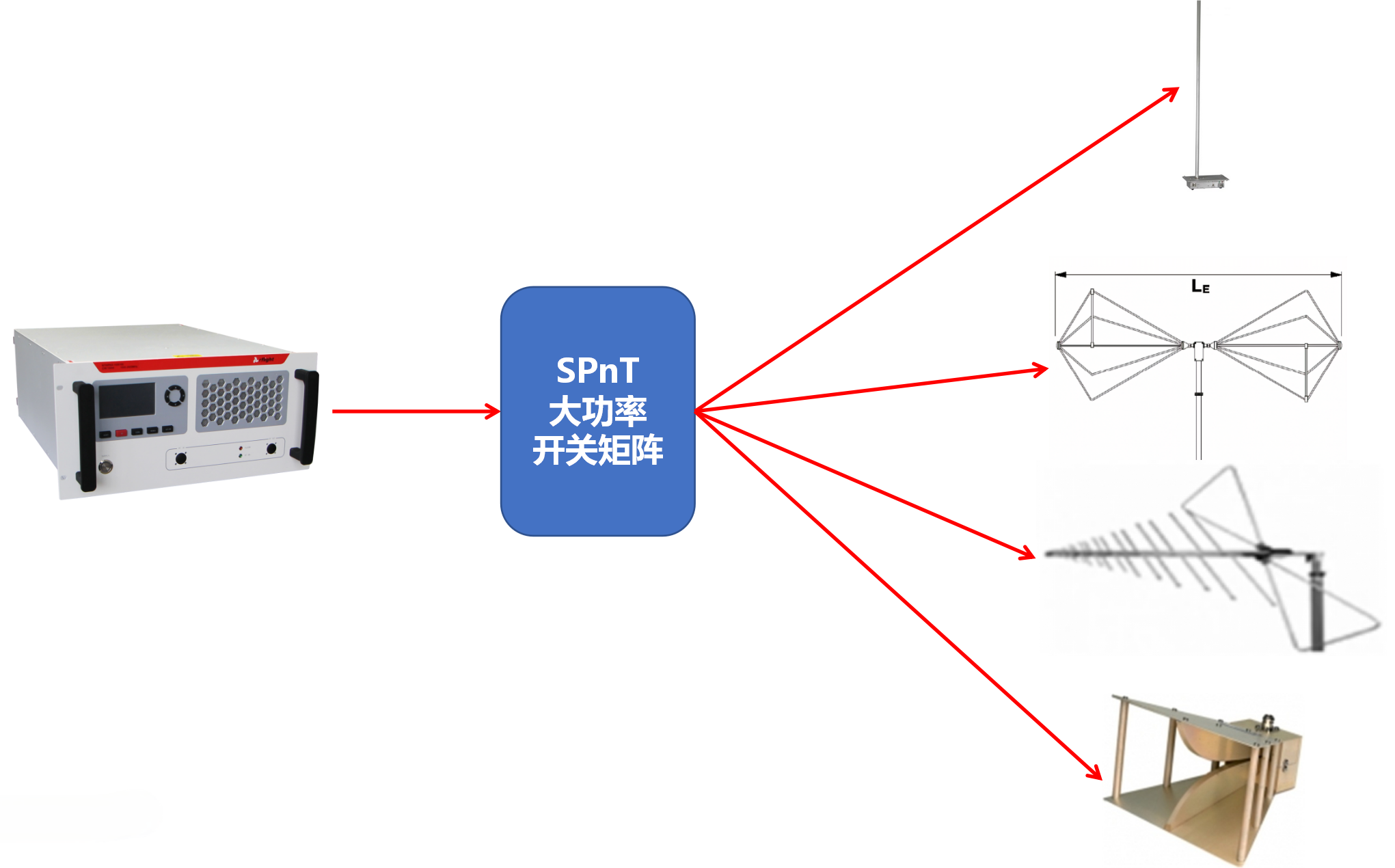



 Record number: Su Gongwang Security 32011502021381
Record number: Su Gongwang Security 32011502021381